本文主要记录了 Java IO 相关的基本操作,涵盖传统IO、Socket、Okio、NIO、AIO,目的是为了以后再遇到 IO 操作相关的需求时,即便忘记该怎么写了,也能通过本文中对应的例子得到启发。对于本文没有涉及到的具有代表性的例子,以后遇到后再补充。
1 IO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| private static void io1() {
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
outputStream.write('a');
outputStream.write('b');
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
往 file 文件写数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| private static void io2() {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file)) {
System.out.println((char) inputStream.read());
System.out.println((char) inputStream.read());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
从 file 文件中读数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| private static void io3() {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader)
) {
System.out.println(bufferedReader.readLine());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
通过 buffer 中读数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| private static void io4() {
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer)
) {
bufferedWriter.write('a');
bufferedWriter.write('b');
//当 Buffered 被关闭时会自动 flush,而 try(...) 写法自动包含了关闭 Buffered 的逻辑,所以可以省略 flush() 方法调用。
//bufferedWriter.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
往 buffer 中写数据,之后保存到文件。
注意: BufferedWriter 中的缓冲的数据量只有达到 8192 个字节才会被刷新一次数据(共 8192 个字节)到文件中,除非你主动调用它的 flush 方法,所以我们从 buffer 写数据到文件中时总是会调用它的 flush 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| private static void io5() {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile)
) {
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int read;
while ((read = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(data, 0, read);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
将数据从 file 文件复制到 outFile 文件。
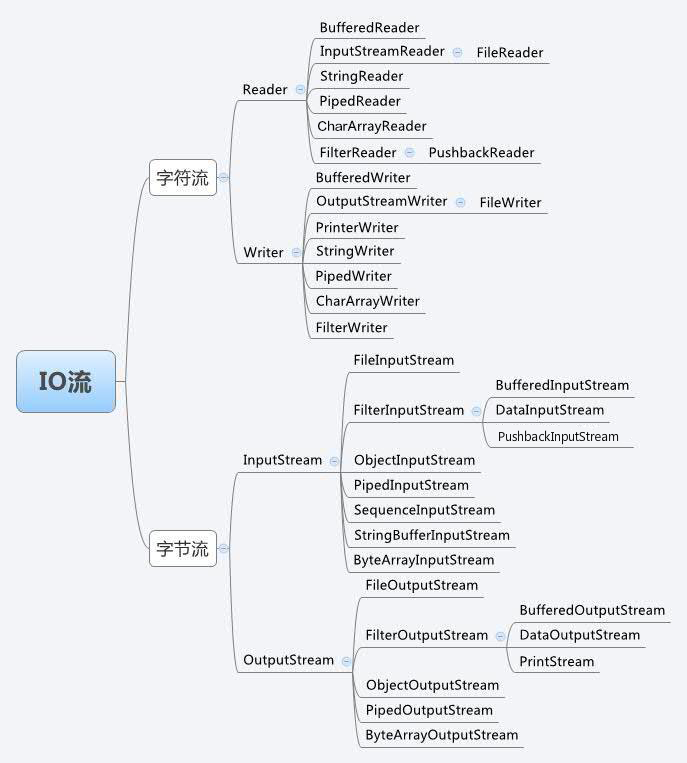
知识补充
File 文件操作可参考 这篇文章 。
2 Socket
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| private static void socket1() {
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()))
) {
String data;
while (true) {
data = reader.readLine();//读取客户端数据
writer.write(data);
writer.write("\n");
writer.flush();//发送数据到客户端
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
服务端代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| private static void socket2() {
try (Socket client = new Socket("serverName", 8080);
OutputStream outToServer = client.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(outToServer);
InputStream inFromServer = client.getInputStream();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(inFromServer)
) {
out.writeUTF("Hello from client");
System.out.println("服务器响应: " + in.readUTF());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
客户端代码。
Socket 基础知识可参考 这篇文章 。
Socket 实际使用可参考笔者的 ITalk项目 。
3 Okio
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| private static void okio1() {
try (Source source = Okio.source(file)) {
Buffer buffer = new Buffer();
source.read(buffer, 1024);
System.out.println(buffer.readUtf8Line());
//也可和传统 io 交互
//buffer.outputStream();
//buffer.inputStream();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
从 file 中读数据到 Buffer。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| private static void okio2() {
try (Source source = Okio.source(file);
BufferedSource bufferedSource = Okio.buffer(source)
) {
System.out.println(bufferedSource.readUtf8());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
从 file 中读数据到 BufferedSource 。
4 NIO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private static void nio1() {
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("text.txt", "r");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel()
) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset().decode(byteBuffer));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
从 text.txt 中读数据到 ByteBuffer 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| private static void nio2() {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int n = selector.select();//这里是阻塞的。
if (n == 0) continue;
Iterator ite = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel clntChan = ((ServerSocketChannel) key.channel()).accept();
clntChan.configureBlocking(false);
//将选择器注册到连接到的客户端信道,
//并指定该信道key值的属性为OP_READ,
//同时为该信道指定关联的附件
clntChan.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
// handleRead(key);
}
if (key.isWritable() && key.isValid()) {
// handleWrite(key);
}
if (key.isConnectable()) {
System.out.println("isConnectable = true");
}
ite.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
Selector 的使用。
参考链接>>
PS:参考链接中 “实现原理” 部分的内容没看懂,后面有时间再研究吧。
5 AIO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| private static void aio1() {
Path path = Paths.get("text.txt");
try (AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel =
AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.READ)) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
long position = 0;
Future<Integer> operation = fileChannel.read(buffer, position);
while (!operation.isDone()) ;
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
buffer.clear();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
同步方式读取 text.txt 文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| private static void aio2() {
Path path = Paths.get("text.txt");
try (AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.READ)) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) fileChannel.size());
fileChannel.read(buffer, 0, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
System.out.println("result = " + result);
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[byteBuffer.limit()];
byteBuffer.get(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable throwable, ByteBuffer attachment) {
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Sleeping for 5 seconds...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
异步方式读取 text.txt 文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| private static void aio3() {
Path path = Paths.get("text.txt");
try (AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.WRITE)) {
String data = "test data";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(data.length());
buffer.put(data.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
long position = 0;
Future<Integer> operation = fileChannel.write(buffer, position);
buffer.clear();
while (!operation.isDone()) ;
System.out.println("Write done");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
同步方式往 text.txt 写数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| private static void aio4() {
Path path = Paths.get("text.txt");
try (AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.WRITE)) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
long position = 0;
buffer.put("test data".getBytes());
buffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(buffer, position, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("bytes written: " + result);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("Write failed");
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Sleeping for 5 seconds...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
异步方式往 text.txt 写数据。
AIO 参考链接>>
